How Much Does It Cost to Replace an HVAC System?
Having an HVAC system in good repair is absolutely necessary. In states like Florida, your AC most likely runs 360 days a year…and on the other five days, you need the heat. And living without heat during January in Kansas City is unimaginable. No matter where you reside, a comfortable home is a must.
So, when your HVAC system fails — and it will — are you prepared for the expense? Let’s take a look at the average cost to replace heating and air conditioning systems and what factors affect the price. Knowing more about how various systems work, where they’re located and their components can help you make more educated decisions about repairs and replacement. And a more accurate estimate of HVAC replacement costs can give you insight into how you can pay for it.
What is an HVAC system and what does it do?
Your heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) system is one of the most important elements of your home. It keeps you cool in the summer, warm in the winter and dry in the humidity. And it filters your air to minimize dust and other particles.
While you may think of your HVAC system as the box outside or the air handler inside, it’s actually an integrated system of many different components that work together to keep the temperature exactly where you want it.
Here are the various parts of your HVAC system:
- Inside component: Inside units, or air handlers, are usually found in a closet or in the basement. The air handler uses a blower to circulate the air inside your home. Air is sucked into the unit, filtered, cooled or heated and blown out through the ductwork. Other components include a furnace, evaporator coils and a wastewater line to remove condensation.
- Outside component: The metal casing located outside contains a compressor, a condenser coil and a fan. Its primary function is to disperse the heat passed through from the air handler. The compressor uses refrigeration lines to circulate a coolant (Freon) between the indoor and outdoor units. These lines cool the air and pull the heat out of your home.
- Thermostat (control component): Located on an inside wall, the thermostat is your control station to set the temperature inside your home. It measures the actual temperature of the air around it and attempts to maintain the temperature throughout the house at whatever you set. However, the temperature can vary from room to room, since different rooms contain different elements, such as more windows or a stove.
- Ductwork (circulation component): The vents in your home, which may be located on or close to the ceiling or to the floor, are connected to a series of conduits called ductwork. Air is carried to and from the air handler unit through these ducts.
How to calculate your HVAC replacement cost
Because a wide range of factors influence the type and size of the best system to meet your needs, how much an HVAC system costs is not usually advertised. That makes it difficult to compare them. Most people rely on an installation company for a cost estimate.
To avoid surprises, you can determine the average cost of furnace and air conditioner replacement for your particular house and make smart decisions about what to buy. This research will help you decide what installation company to hire.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average cost to replace heating and air conditioning can vary between $4,000 and $20,550 for the equipment. The cost variance depends on what components you need; the size, quality and type of equipment; and the size of your house in square footage (sometimes it helps to calculate an HVAC system’s cost per square foot for context). Installation costs on top of that can take a few hours or several days. Naturally, a lot of ductwork replacement will result in higher labor costs.
Realistically, with equipment and installation costs factored in, the average cost to replace heating and air conditioning can easily run well over $15,000, especially if ductwork needs to be replaced or added.
The good news is that a new system can last up to 22 years with minimum maintenance. Here’s what you need to know to narrow down your price range.

Determine what type of HVAC system you own
One factor in determining the average cost to replace heating and air conditioning is the kind of HVAC system you have or want. There are four main types of HVAC systems:
- Split HVAC systems.
This type of HVAC system, also known as a heat pump, is the most common type of whole-house solution. It has separate units for heating and cooling. The cooling system is outside the house and consists of a ventilated housing with a compressor, a fan, refrigerant lines and coils. Its job is to remove heat from the house and vent it outside.
The heating element, or furnace, is usually located in the basement. In warmer climates, the furnace is smaller and is part of the air handler unit located in a closet. The furnace may be gas or electric, and it is designed to circulate heated air through the ductwork system.
If it requires extensive ductwork, installation costs can be high. The HVAC system cost to replace just the indoor and outdoor equipment for a 14 SEER split system will cost around $7,500 or more. While the initial investment is higher than average, heat pumps could pay for themselves in savings on energy costs.
- Hybrid HVAC systems.
Also known as dual-fuel systems, hybrid HVAC systems are most common in homes located in warmer climates. The equipment costs more upfront but could pay for itself many times over in lower operating costs.
With a hybrid system, an electric heat pump is supplemented by a gas furnace. When the temperature drops below 40 F, electric heating costs can go through the roof as your heat pump struggles to warm your house. By setting the temperature at which the gas furnace kicks on, you’ll save money and stay toasty, even in the coldest weather.
For a 2,000-square-foot house, the average price is about $8,500. A house that big would then have an HVAC system cost per square foot of $4.25.
- Mini-split (or duct-free) HVAC systems.
Mini-split systems don’t require ductwork. Individual room units are connected directly to an outside unit, allowing you to control the temperature in separate rooms. While they don’t require duct installation, the equipment costs for individual units can run high.
Depending on the size of your home and number of units you want, you could expect to pay around $4,000 for a smaller home, up to more than $15,000.
- Packaged HVAC systems.
Packaged HVAC systems are fairly rare. They depend on a single unit with all the components for heat and air inside an outside housing. They can be either a heat pump or a hybrid system. Since they require only one location and no onsite assembly, installation costs are usually lower than with other types of systems. But with all the components exposed to the elements, they require more frequent maintenance.
With installation, a packaged system is likely to run you around $7,000, but can often exceed $10,000.
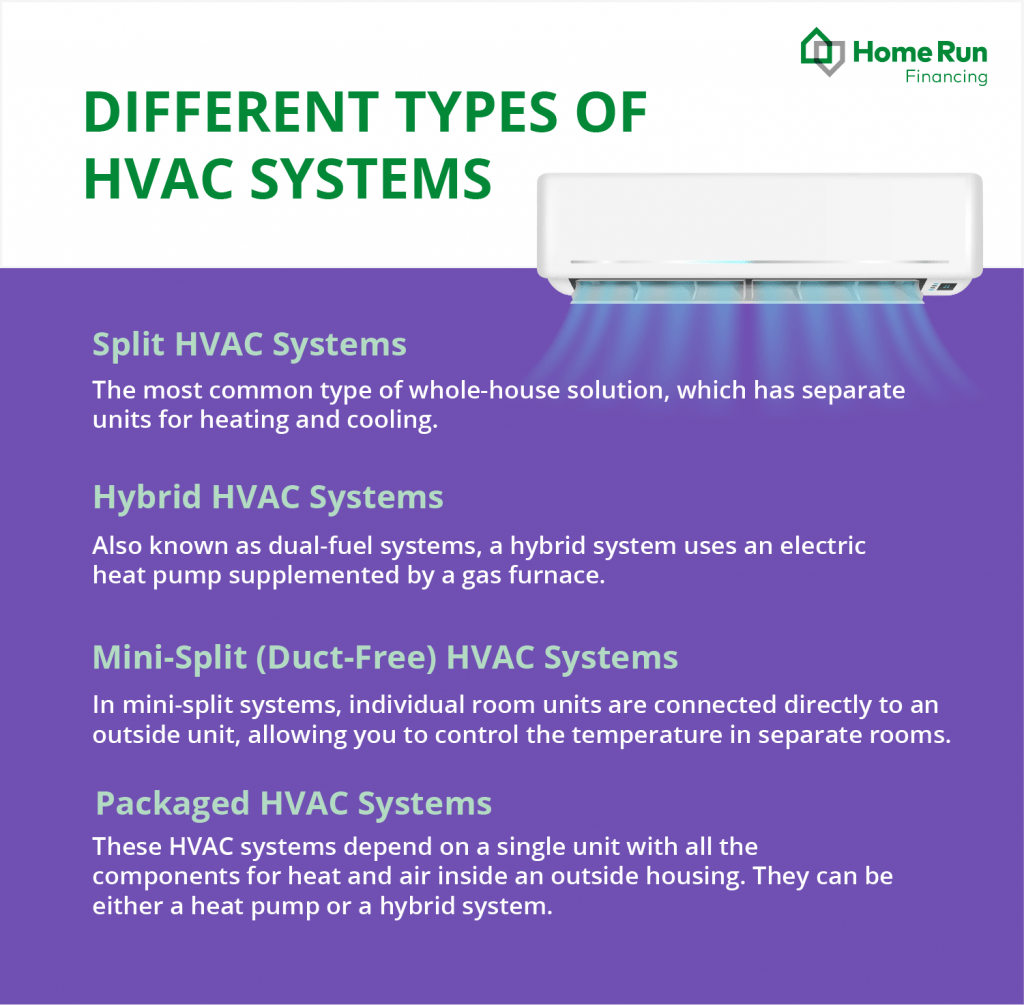
Figure out what parts you need replaced
When your air suddenly stops working, you may not have to deal with the full HVAC replacement cost. Depending on the age and condition of your system, you may be able to repair or replace individual components. Here are the parts of the system and the cost of replacement for each.
Indoor HVAC unit parts
- Blower assembly. Inside your HVAC air handler, the blower circulates the warm or cold air via the ductwork and through the vents with a small motor attached to a fan. Motor and fan replacements are fairly inexpensive repairs. The motor should run no more than $200, with a fan costing up to $100 plus installation.
- Ductwork. Ductwork connects to your HVAC system and carries the heated or cooled air throughout your house. Ductwork for your HVAC system cost per square foot depends on the cost of labor in your area, the type of ductwork material used and the difficulty of the job. As a rule of thumb, ductwork will cost up to $20 per linear foot. It can be a major HVAC replacement cost, but the need to replace your ductwork system is rare. Bear in mind, when you have ductwork replaced, other issues may arise that lead to additional costs. You may need to replace drywall, for example.
- Evaporator coil. The evaporator coil is usually located in the air handler. Its function is to absorb the heat from your house. A replacement evaporator coil for a small unit runs about $150 or less. Large units can cost $1,200 or more, plus installation.
- Furnace or air handler. In your HVAC system, the furnace is the component that heats the air before it is circulated through your home. The price of replacing a furnace varies by brand, home size and installation costs. The average cost of a new furnace runs between $800 and $3,500 plus installation. It’s usually a good idea to replace the indoor and outdoor units at the same time.
- Thermostat. The thermostat is the electronic device you use to moderate the temperature in your home. The thermostat continuously monitors the temperature and turns the heat or AC on and off to maintain the temperature you set. Thermostats are a relatively inexpensive part of the HVAC system. The cost of the equipment runs from $20 to upward of $500 for a smart, integrated thermostat with all the bells and whistles. Plus, factor in the cost of professional installation.
- Wiring. Naturally, these electrical components are all connected by electrical wiring. In some cases, your wiring will need to be replaced. While the cost of wire is negligible, a service call usually runs from $100 to $250, plus $50 to $100 per hour.
Outdoor HVAC unit parts
- Condensing unit. When refrigerant circulates through your HVAC system, the compressor pressurizes the liquid into a gas and pushes it through refrigerant lines to the inside components and back outside to the condensing unit. The condensing unit converts the gas into a liquid and releases the collected heat. The cost of replacing the condensing unit depends on the size and brand of the unit, which starts at under $200 for the coils alone and can be more than $3,000 for the unit plus installation costs.
- Compressor. Located in the housing outside, the compressor is the part of your air conditioning unit that circulates refrigerant (Freon) through the HVAC system. As it circulates, the refrigerant liquid pulls the heat outside to the condenser coil, where it can disperse. Price depends on the size of the unit and the brand. The smallest units on the market start around $650 plus installation costs.
- Fan. HVAC fans are composed of two relatively inexpensive parts, the motor and the blades. The fan motors average between $100 and $200, and fan blades run $50 to $100. Optional parts used to protect the fan, like leaf guards and protective covers, run about $50.
- Heat exchanger. When a heat pump is engaged, the condensing unit process is reversed: Heat from outside is drawn in through the refrigerant lines and released into the air handler, where it is dispersed into your house. Heat exchangers cost between $100 and $1,200 plus installation.
- Refrigeration lines. The most common issue with refrigeration lines is a Freon leak. If you have a Freon leak, it could cost up to $1,500 to find and fix the leak and recharge the system with Freon. The ultimate cost depends on where the leak is located, the age of your unit and the labor rates in your area.
Establish what size HVAC system you need
You may think a bigger HVAC system will do a better job of heating and cooling your home, but that is not the case. The correct size for your new HVAC installation depends on the size of your home and its insulation and ventilation. Your location is another factor: People who live in hot, humid climates need more cooling power and have higher cooling costs than people who live in a cold climate.
All air conditioners come with a Btu rating. Btu stands for British thermal unit. One Btu is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of a pound of water by 1 F. HVAC cooling power is measured in tons, and it has nothing to do with the weight of the unit. In northern climates, a typical central HVAC system has 36 kBtu/h and a seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) of 13.9. In hot, humid Southern states, a typical central HVAC system has 36 kBtu/h and a SEER rating of 14.4.
Choosing an HVAC system that’s the right size for your home is crucial to energy-efficient performance. If it’s too small, your air conditioner will run constantly. Your energy bill will be sky-high, and all the rooms in your house will rarely be comfortable. Excessive wear and tear will shorten the life of the unit, and you’ll end up spending far more in the long run. That’s why you should not base your decision on cost. On the other hand, if you buy a unit that’s too big, it will cool the nearest areas quickly and shut down, leaving more remote rooms too warm.
Decide on your desired energy efficiency rating
The efficiency rating for HVAC systems is measured with a seasonal energy efficiency ratio, or SEER rating. It’s determined by dividing the cooling output of the unit during the peak-use summer season by the energy, measured in watt-hours.
Today’s air conditioning units have SEER ratings from 13 to 25. Higher SEER ratings mean greater efficiency and lower energy bills. While HVAC units with higher SEER ratings will cost more upfront, many consumers recoup the extra money spent on their monthly bills.
Consider the physical placement of your HVAC system
The last thing to consider when figuring HVAC installation cost is where the system components are located. Project difficulty can add days of labor costs. Expect to pay more if components of your system are located in the attic, crawl space or other area that’s difficult to access.
Funding your furnace and air conditioner replacement
Calculating an HVAC system’s cost can be difficult, and labor-intensive jobs can result in unexpected charges. It’s always a good idea to get several price quotes and check online reviews before hiring an HVAC professional.
Now that you have an understanding of the average cost of furnace and air conditioner replacement, it’s time to consider how you’ll pay for your new system. Most of us don’t have that kind of money sitting around in case of emergency.
There are plenty of options to pay for expensive home repairs, and Home Run Financing is one of the most sensible home improvement financing options, whether you’re trying to beat the heat in Miami or Southern California, or keep warm during a blizzard in Kansas City. When you work with Home Run Financing, you leverage the equity in your home without losing your investment. You don’t need good credit to take advantage of this program, and approval is fast and easy. Since you set the length of time to pay back the loan — and interest rates are lower than almost all other types of credit — your payments will be affordable. Learn more about air conditioning replacement financing and other Home Run Financing options today!
